It’s all about front-end guides for web designers and developers. But to most its just bootstrap, foundation, uikit, materializecss, concisecss or any other with which they are comfortable. But big companies usually work with there own front end design guideline which they use it to design their websites, apps. So what is the best way to design a killer front end design guide, well here is it. Here are some key points that should be present in any front end design guidelines.
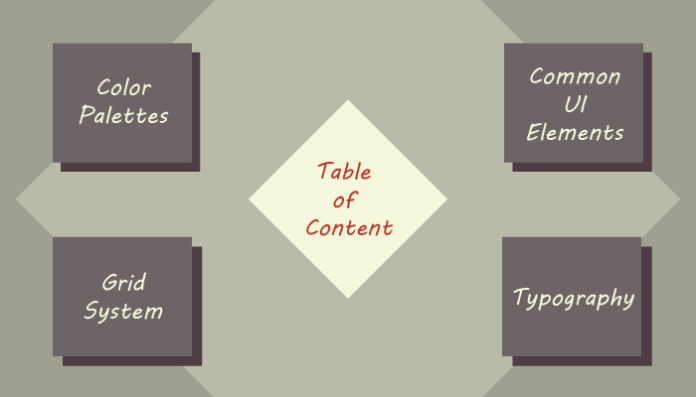
- Table of content: The most important is the Table of content. This will allows the users to surf throw your guidelines easily and this will actually act like a sitemap to your design.
- Common UI Elements: that is the heart of any front-end style guide. For.e.g Grid-Layouts, Buttons, Breadcrumbs, navigation and modal dialog and there behaviors. These elements can be of static and dynamic nature (in terms of behavior).
- Static elements are those that can be designed and coded through the HTML and CSS and not involving any JavaScript. These elements are mostly basic elements like form elements, accordions, dialog boxes and others. Pretty much any tools that can be manipulated with CSS.
- Dynamic elements are the ones which involves the JavaScript, They are more detailed and more behavioral elements like Opening of Dialog boxes, Drop down elements of navbars, Accordions, Tabs, Tool tips, Main sliders, Carousels and it could be certain plugins like reducing the size of the header logo on scroll and many other cool stuff. In simple term they put life into elements and define there behaviors.
- Color Palettes: Just like brand guide-line’s Color palette, that allows the users to understand the colors of the company, Front end color palette is a must for to represents how the company’s presence will looks and feels like on the web.A proper Color palette of the company must be present including the colors for UI Elements must be defined. This is a great help for the designer and developers “who are lazy” lol.. to pick and use instantly.
- Grid system: This is a layout system that defines how each element will be organized on screens. Both for responsive or adaptive designs this helps to decide how the element will be placed. Grid systems are responsible for the block structure of the web.Most common examples to understand this is the 12-column,16-column. Although, thanks to bootstrap 12-column is mostly used in websites today.
- Typography: Type is one of the key element to share meaningful information, not just for human users but also for the Search engines to index your web. Here you only have to worry about the first party that is human users. Typefaces, sizes, weights should be well structured and defined for (paragraphs, headings, quotes, image captions)
Before anyone files plagiarism case here is the original article that inspired me to write. The following article handsomely explain what front-end guide lines are. I encourage everyone to go and have a read.
Reference: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/front-end-style-guides/